Imagine you’re having dinner and your phone rings with an important mail from work. The voice assistant reads the mail out without even touching the device. Now imagine composing a reply to that mail in the same way, only through speech! Sounds fascinating, right? Both situations are not a daydream today – thanks to text to speech and speech to text technologies.
Technological transformation has simplified several complex activities alongside improving human-machine interaction. Innovations like text-to-speech (TTS) and speech-to-text (STT) have significantly contributed to such advancements. Notably, the text-to-speech (TTS) global market size was valued at $4 billion in 2024, which is set to go beyond $7 billion by 2029. Conversely, speech-to-text is also getting increased attention with an enhanced integration rate.
But how does text to speech and speech to text technologies differ from each other? Let’s find out…
An Overview of Text-to-Speech (TTS):
Text-to-speech (TTS) tech typically converts digital text into voice-enabled speech. It belongs to the category of assistive technologies that help devices to read written texts aloud. One example of TTS is digital audiobooks, which can be read out loud by any digitally available books and help learners. This technology utilizes advanced neural networks and deep learning methodologies to formulate natural voices for the text provided.
TTS can be used and be beneficial to address literacy challenges, assist the visually impaired, enhance customer service, empower smart devices, help in public transportation announcements, and others.
Types of TTS:
Below are the major types of text-to-speech technology-
Built-in text to speech: Several devices, like mobile phones, have built-in text to speech technology.
Tools on websites: Integrated with websites like virtual assistants.
Third-party applications: Users can download or install these tools on their devices.
How does Text-to-Speech Work?
Text-to-speech tech is generally integrated with different types of devices, including mobiles, laptops, tablets, and others. It operates following several stages, including text analysis, text conversion, voice synthesis, and others.
Primarily, TTS tech analyzes the provided text that needs to be converted. The goal behind analyzing the text is to comprehend the meaning and structure it holds. The following stage is linguistic processing, where the text becomes the phonemes so that a device can pronounce a text.
After understanding how to pronounce a word, an element of linguistic processing assesses the appropriate tone and rhythm that makes the speech sound natural. The last and most important stage includes voice synthesis, where a device gets the ability to produce speech just like humans.
Understanding Speech-to-Text (STT) Tech:
Speech to text (STT) is a voice recognition and conversion mechanism that is used to convert verbal speech and spoken words into text. Several mechanisms, such as large language models, machine learning, and deep learning algorithms, work together to enable devices to understand speech and convert it into text.
STT majorly relies on AI-driven speech recognition technology, or automatic speech recognition. One of the examples of such an approach is voice search on browsers. With speech to text in browsers, users can just ask their queries verbally, get results in text, and browse different websites. Such technologies can be used in various fields, including the transcription of live events, sales intelligence, research and development, e-learning, and more.
Types of STT:
Speech to text tech can be segmented into two types-
Speaker-dependent: Usually integrated with dictation applications.
Speaker-independent: Integrated with mobile applications.
How does Speech-to-Text Work?
Speech-to-text tech uses various aspects, including speech input, feature extraction, decoder, and word output, to operate. Primarily, it initiates audio processing, through which the recorded voice is assessed and processed for quality improvement. The following phase includes sound analysis through which the speeches are broken into phonemes, separating each word.
The next stage is feature extraction, where the system identifies the different patterns and emotions of each word. While decoding the output, STT algorithms use language models to replicate the speech features. Finally, in the last phase, the text version of a speech is presented in an understandable and readable manner for humans.
Identifying the Differences Between Text to Speech and Speech to Text:
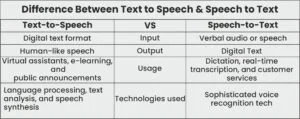
Text to speech and speech to text enhance human-machine communication but hold several differences. The common dissimilarity is that the former converts text into speech. On the other hand, speech to tech converts verbal inputs into text output. Let us discuss other crucial differences between text to speech vs. speech to text-
Different Inputs:
Text-to-speech requires input or prompts in text format. So, TTS can only operate when the input is in text. On the other hand, speech-to-text needs input or prompts in vocal audio or speech format.
Different Outputs:
Text-to-speech generates output in audible speeches, whereas speech-to-text generates digital text as output.
Usage:
Text-to-speech is incorporated for various activities, such as virtual assistants on devices, e-learning, announcement-making, and more. Conversely, speech-to-text is useful for activities like video transcription, dictation, customer service, language learning, etc.
Technological Considerations:
Text to speech and speech to text depend on different technologies to function. The former leverage language processing, text analysis, and speech synthesis methods. On the other hand, STT utilizes sophisticated voice recognition tech.
How to Choose the Best Text to Speech and Speech to Text Tools?
While choosing the right TTS or STT tool, users need to look after the following components-
Accuracy Parameters: Ensure the accuracy level of the tool primarily. The user expectations cannot be met if the tool fails to generate accurate outcomes.
Compatibility: Consider whether your TTS and STT tool is compatible with different devices and can fulfill diverse needs.
Language support: Standard TTS and STT tools offer multi-language support. Hence, ensure your tool is meeting this parameter.
Concluding Remarks on Text to Speech vs. Speech to Text!
Text to speech and speech to text both use AI capabilities to assess, analyze, and convert prompts in different formats. The former converts text into speech, and the latter converts speech into text. Such technologies doubtlessly boost human-machine communication. Nevertheless, both possess certain limitations.
The gap in generating appropriate human-like voices is still present in text-to-speech technology. On the other hand, speech to text tech encounters challenges in understanding and transcribing different accents within a language. Therefore, it is important to consider these concerns before adopting TTS and STT. Appropriate deployment and usage of these technologies can address language barriers in a broader sense alongside boosting customer experiences and transcription.
Was the blog informative? If so, then read our other in-depth blogs at YourTechDiet!
Also Read:
A Guide to Multimodal Machine Learning (MMML): Integrating Sight, Sound, and Text
Voice Recognition Technologies vs. Speech Recognition Technologies: Understanding the Differences