Money and finance have continually changed from the barter system through paper currency, then credit cards, now digital wallets, and all the way to cryptocurrency. Such evolution describes the human pursuit of continually efficient and safer ways to exchange value.
Cryptocurrency, the latest notch on the belt of this financial evolution, is reformulating money concepts. Like fiat currency, cryptocurrency operates on decentralized networks supported by blockchain technology.
But then, what is cryptocurrency, how does it operate as it does, why is it worthy of cash and attention by investors and even governments alike? Are we in the largest financial revolution of our age? A better understanding of disruptive technology and the forces working in its favor may answer this question.
What Is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency, the mode of digital currency for the new era, uses blockchain technology for online digital transactions. Although there are thousands of cryptocurrencies operating today, Bitcoin, Ripple, Ethereum, and Litecoin are somewhat popular. It only exists in a digital format, is cryptographically secure, and can be used for everything from online payments to investments.
Data shows that there are today thousands of cryptocurrencies, but the first and most popular one is Bitcoin, which was created in 2009 by a creator with a very imaginary name-Satoshi Nakamoto. Gradually, thousands of other digital currencies came into existence, launching the financial revolution.
Since cryptocurrencies operate using blockchain technology, it will be nearly impossible to duplicate and counterfeit them like paper money. All transactions are verified and recorded and thus represent a big step toward a decentralized and digitized future of finance.
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
Cryptocurrency sustains its operation through blockchain technology. Blockchain is a ledger that is decentralized in nature. It is used to record all transactions. Cryptocurrencies are independent and work over a network of computers. Such a network is called a node.
The nodes work together to confirm and store transactions in a secure manner. When a transaction occurs, it is added to a block of data. This data structure ensures that all transactions are open, secure, and non-alterable. Therefore, it becomes fraud and tampering resistant.
Users should have digital wallets into which they can be sent, received, and/or stored. Such wallets have a public key and a private key. Whereas the user’s public key is comparable to an account number, the private key is the password for that account. When a transaction is made, the sender signs it with their private key, while cryptography confirms the transaction on the network.
Numerous cryptocurrencies also resort to a procedure known as mining or staking. In mining (as used by Bitcoin), powerful computers solve extremely complex mathematical challenges to authorize transactions and add them to the blockchain. In staking (employed by Ethereum 2.0 and others), users lock away their cryptocurrency to contribute to network security and reap benefits in exchange.
What Makes Cryptocurrency Valuable?
Cryptocurrency values are like those of any commodities; they are dependent on supply and demand. Supply is simply the quantity of available cryptocurrencies. With less supply, their prices may tend to go high. This is offered/requested for and by people. If many people would like to buy Bitcoin, that price will increase. If fewer people want to acquire it, maybe it would be less valued.
Cryptocurrency values, besides being tradable, are just the nature of each various cryptographic measure whether it be getting more people to invest in the future of crypto, enjoying cheap transactions when using Bitcoin, or simply supporting a new system of currency.
Cryptocurrency has little or no requirement for personally identifiable information, unlike most traditional intermediaries. Some cryptocurrencies offer enhanced privacy and anonymity features. Even though transactions are supposed to be recorded on a public ledger, tracing them becomes a nightmare.
The process of guaranteeing the safety of virtual currency transactions is situated in the cryptographic structure thereof. Cryptography controls the production of additional units of currency. The encryption process prevents other persons than the rightful owners from accessing cryptocurrencies. There are fewer chances for life and active fraud, forgery, and unauthorized access. Transactions are always verifiable and secure because they are run on a decentralized blockchain.
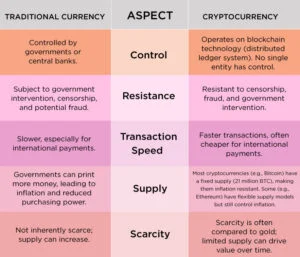
Cryptocurrency vs. Traditional Currency
The battle between traditional currency and cryptocurrency has sparked a global conversation about the future of money. How do these two forms of currency truly compare? Let’s break it down.
| Aspect | Traditional Currency | Cryptocurrency |
| Control | Controlled by governments or central banks. | Operates on blockchain technology (distributed ledger system). No single entity has control.
|
| Resistance | Subject to government intervention, censorship, and potential fraud.
|
Resistant to censorship, fraud, and government intervention.
|
| Transaction Speed
|
Slower, especially for international payments.
|
Faster transactions, often cheaper for international payments.
|
| Supply
|
Governments can print more money, leading to inflation and reduced purchasing power.
|
Most cryptocurrencies (e.g., Bitcoin) have a fixed supply (21 million BTC), making them inflation resistant. Some (e.g., Ethereum) have flexible supply models but still control inflation.
|
| Scarcity
|
Not inherently scarce; supply can increase.
|
Scarcity is often compared to gold; limited supply can drive value over time.
|
Challenges Associated with Cryptocurrency
Lack of regulation: Most governments have hardly scratched the surface in determining how to regulate cryptocurrencies. Doubts are developing within the market over the viability of this form of financial resource. While some countries legally recognize and sanction its use, others have just as quickly banned or restricted it. What is more troublesome is that fraud, money laundering, and tax complications still remain matters of concern for most users and governments alike.
Limited Acceptance and Wide-Use: Not that they are gaining popularity, but cryptocurrencies are not yet very widely accepted as a means of payment when compared to actual money. Many businesses, governments, and financial institutions remain skeptical or hesitant to adopt them. This is attributed to their susceptibility to volatility and regulatory issues. Cryptocurrencies have not achieved mainstream success. The mass adoption seems to be a challenge.
Association with Illegal Activities: Because of the relative ease of anonymity and privacy provided by cryptocurrencies, they are being allegedly associated with so many illegal actions. Examples include money laundering, tax evasion, and ransomware attacks. Although most crypto transactions are legal, this continuing association with criminal acts has led to even tighter restrictions and monitoring by some countries.
What Does the Future of Cryptocurrency Hold?
Another big reason for controverting the current stand of unregulated cryptocurrencies is that they are currently gaining huge popularity. Countries accommodate cryptocurrencies within clearly established practices of regulation. Under this gauntlet, Japan and Switzerland have such regulations. On the other extreme, China takes a starker approach-unrestrictedly banning cryptocurrency trading and mining.
However, some strike a balance between oversight and innovation, with countries exemplified by the United States and the European Union. Regulatory measures being instituted in these jurisdictions include crypto exchange licensing and stricter reporting standards.
The Close cryptocurrency is possibly at a crossroads because the majority of states are coming up with a more defined regulation while technological advancement is on the rise. It has changed to match the expectations of an increasingly digital world and is no longer only an investment vehicle as it used in the past.
Will it indeed alter how we transfer and store wealth and hence begin to lay the foundation of a new global economy? Or will it just have a much softer and synergistic role with the traditional currency to execute digital payments without largely, if not entirely, replacing what we now have? It is certain that cryptocurrencies have a bright future ahead of them, and their influence on business, money, and common transactions is only now beginning.
To learn more about cryptocurrency or blockchain technology, visit us at YourTechDiet!
Read More:
The Rise of Cryptocurrency and its Impact on the Global Economy