Since the last decade, Cloud Computing has been one of the critical technologies that storm the world. Companies and many other businesses have started to push their workload to remote servers.
One of the problems that cloud computing often doesn’t handle well is a time delay. While processing data in the cloud, there is bound to be some delay between uploading data and downloading results from data.
The lapse in time can create issues in the time-critical systems. Network architects are proposing architectures and network designs where the computing power is distributed evenly to provide full service to deal with this problem.
Two such cloud architecture is Fog Computing and Mist Computing architectures.
In this Fog and Mist Computing blog, I will give you an idea of how these two Business Intelligence tools differ from one another.
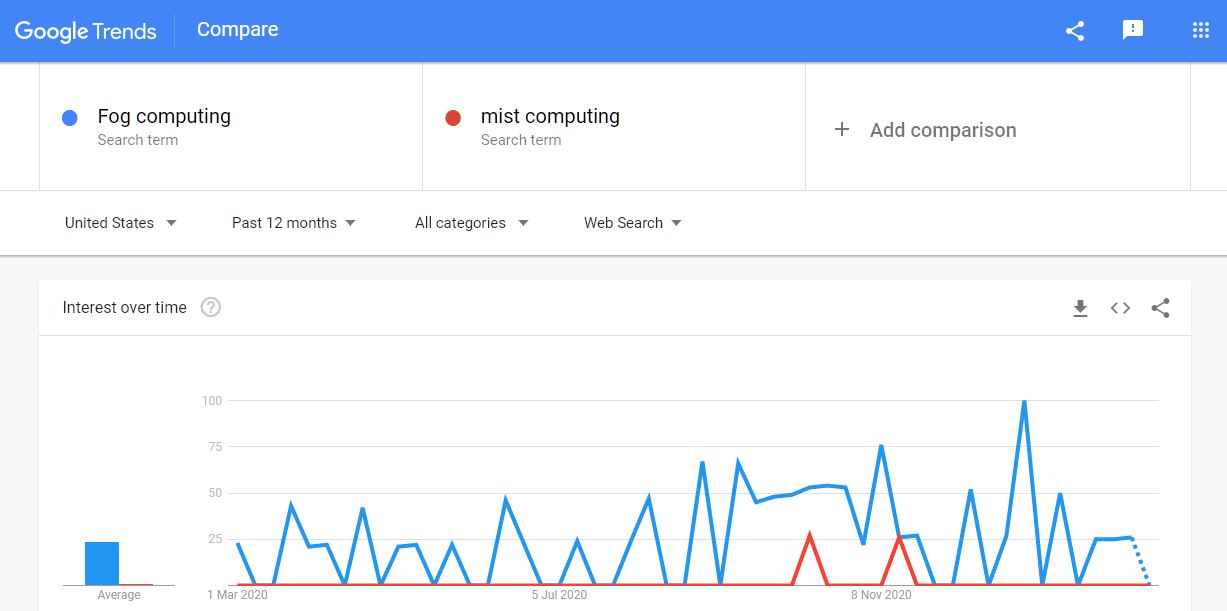
Fog Computing vs. Mist Computing: Which is more popular?

From the above Google Trends screenshot, one can evaluate that Fog Computing is way ahead of Mist Computing in terms of customer preferences.
Difference Across Parameters
- What is Fog Computing?
- What is Mist Computing?
- Key Differences between Fog computing and Mist Computing
- Fog vs. Mist Computing Comparison Table
What is Fog Computing?
Cisco created fog computing. The focus was to increase cloud computing capabilities.
Fog computing is the notion of an idea for a network architecture that expands from the fundamental cloud’s outer edges.
In general, the cloud is where data is created, managed, and eventually to be stored. Mung Chiang, one of the United States’ leading researchers on cloud computing, gave quite a brief idea of fog computing:
“Fog provides the missing link to data needs to be uploaded to the cloud, and what can be analyzed locally, at the edge.”
Fog computing is a network architecture that connects data creation to data storage, whether it is the cloud or the client’s data center.
The architecture includes various elements like servers, storage, and cloud services. Fog computing is seen as an add-on to the cloud, to the network’s edge.
It allows decentralized computing devices to process data at the fog node. Hence, all device-efficient storage, computing, and network connectivity can be used as a fog node.
Pros of Fog Computing
- Real-time data analysis
- Take quick action
- Sensitive data remains inside the network
- Cost-saving on storage and network
- More scalable than Edge computing
- IT/OT teams can manage operations
The Disadvantage of Fog Computing
Fog computing relies upon many links to move data from the physical asset chain to the digital layer, which is a potential issue.
What is Mist Computing?
Mist computing could be a possible solution to lessen the gap between central cloud and edge computing.
A mist device is an enhanced edge computing & fog device with qualities like professional cloud servers.
For example, mist devices can:
- Do local analytics and decision-making using data from the database.
- They are learning and adapting machines like ML and AI.
- Flexible and Robust mechanism.
- The root module is like HSM modules found in a cloud server.
- Data access control capabilities to enforce privacy with the consent at a security level and privacy by architecture.
Mist and Fog computing complement each other as offline and online usages are correlated to each other.
Mist computing uses the sharp edge of a cloud that consists of micro-controllers and sensors.
Operation at the extreme edge allows mist computing to gather resources with cloud networks and communication facilities accessible on the sensor.
Pros of Mist Computing
- Local Decision-making data
- Works with fog computing and cloud platform
Cons of Mist Computing
As Mist computing is still new to the system and the latest cloud technologies, it doesn’t have any proven disadvantage yet.
Key Differences between
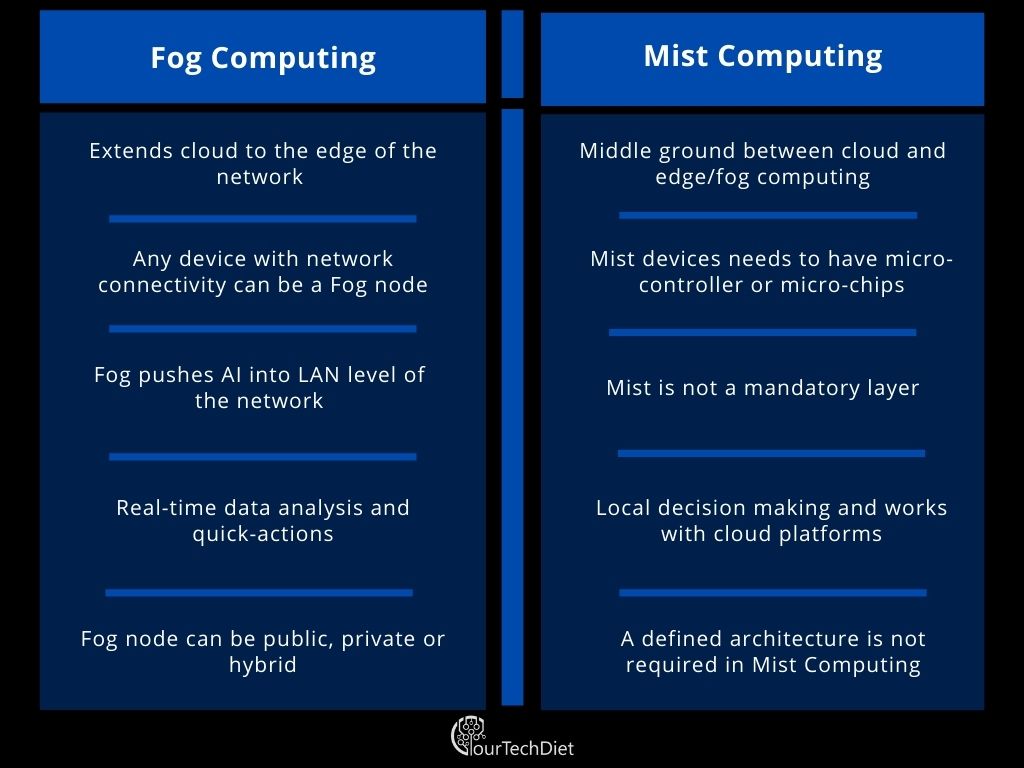
Fog computing extends from the cloud to the edge of the network. In comparison, Mist computing is the middle ground between cloud and edge/fog computing.
Here, any devices with computing storage and network connectivity can be a fog node and put on a railway track or petrol pump.
In comparison, Mist computing is the lightweight computing in the network web using simply micro-controllers and micro-chips.
Fog pushes intelligence down to LAN of the cloud architecture, whereas in Mist, it is not mandatory.
Fog vs. Mist Comparison Table
Conclusion
Through this comparison between Fog and Mist Computing blog, organizations need to understand that fog computing and mist computing have their own set of strengths and disadvantages.
Understanding and using these standards will ensure that the growing number of IoT devices can work reliably. Also, businesses can combine Fog and Mist computing to use their strengths and lessens their constraints.
Various architectures complement each other, and businesses should use such techniques. This will help create a secure, reliable, and highly functional IoT solution.
Also Read:
Fog Computing vs. Cloud Computing: Difference between the two Explained