A computer system’s primary and secondary storage provides the fundamental functions offered by these two data storage services. Data storage offers a hierarchy solution to access computer or system resources. The system stores all the required information with the help of several techniques that leads to data storage levels. System storage has two types such as primary storage and secondary storage.
Computer memory uses to store information in memories. It has four main categories: CPU register, Cache memory, Primary memory, and Secondary memory. The common difference between the primary memory & secondary memory is that the CPU or Central Processing Unit can directly access the main memory. Moreover, secondary memory cannot access by the CPU.
IBM says, “Users can enter the input data directly into a computer. However, they have found early on in the computer era that continually entering manual data is time- and energy-prohibitive. One short-term solution is computer memory, also known as random access memory (RAM). But its storage capacity and memory retention are limited. As the name suggests, read-only memory (ROM) is the data that can only be read but not necessarily edited. They control a computer’s basic functionality”.
Primary memory is nothing but the main memory where the essential processing data is available. Secondary memory is an auxiliary memory where we can store the information permanently. Here in this article, we will learn more about primary and secondary storage with their common difference.
Data storage refers to any techniques and tools used to record and keep digital data on magnetic, electronic, or silicon-based storage devices. Cloud services, edge locations, remote locations, and private properties all need storage. Mobile products like smartphones and tablets need storage as a critical component. Storage is a resource that both consumers and organizations use to protect the information, from intimate images to data that is essential to their operations.
According to Wikipedia, “Computer data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers. A computer’s central processing unit (CPU) manipulates data by performing computations. In practice, almost all computers use a storage hierarchy, which puts fast but expensive and small storage options close to the CPU and slower but less expensive and larger options further away. Generally, the fast volatile technologies (which lose data when off power) are referred to as “memory,” while slower persistent technologies are referred to as storage.”
Primary storage is also known as the main memory of computer system. Data access is quicker from primary memory because it is a computer’s internal memory. It is volatile memory. If data is not stored during a power outage, it does not reside in primary memory. Cost-wise, primary memory is more expensive than secondary memory. It has a much lesser capacity than the secondary memory and is severely constrained.
A semiconductor memory or primary memory serves as the main memory. When compared to secondary memory, it is more expensive. Primary memory has a minimum storage capacity and is always smaller than secondary memory. It stores information that the central processing unit can access directly.
There are two types of Primary Memory:
- RAM
- ROM
RAM (Random Access Memory):
RAM is the primary memory of a computer system. Also, it is the main memory of a computer system, and hence, it is known as cache memory. Further, we can also call it a temporary memory. If the computer is unexpectedly turned off, the data in this memory is gone. RAM is kept in computer chips for quick, minimally if not instant, access. It is a fast data storage media that communicates with the processing unit directly over the memory bus, allowing running algorithms to do so.
ROM (Read Only Memory):
Read-Only Memory or ROM is permanent memory, and when the PC suddenly shuts down, its data is not lost. The device’s maker chooses the information in this memory. Also, it is permanently saved at the time of production and cannot be cleared by the user. PROM is an advanced form of ROM that can be programmed once after it has been made. Read-only memory is the volatile memory that functions between the central processing unit.
Characteristics of primary storage
- Firstly, the computer cannot function or run without primary memory.
- Secondly, it is the main memory of the computer system.
- Thirdly, if the power is lost, you could lose data.
- Another name for primary memory is volatile memory.
- Primary memory is the working memory of a computer system.
- Lastly, primary memory is faster than secondary memory.
Another excellent option for memory storage in a computer is secondary storage. Secondary memory or secondary storage refers to all hardware and software that can store large amounts of data. It is slower than the main memory. Moreover, you can store much information in GB (Gigabyte) to TB (Terabyte) with secondary storage. Further, the alternative names for secondary memory include backup storage and mass storage medium.
They are non-volatile, sometimes known as external memory, which is different from primary storage in that the central processing unit cannot directly access them. Regarding accessing data, secondary storage is somewhat slower than prior storage devices because the I/O channels do not directly access them.
However, the ability to permanently store software and programs makes it one of the most significant assets in the data storage hierarchy. It’s a long-term storage option that increases the data storage capacity, just like the Random Access Memory RAM.
Mass storage devices:
For both small and large devices, the magnetic disc is a mass storage system that offers affordable storage. Two categories of magnetic discs exist Floppy discs, and hard drives are second.
Flash/SSD:
SSD stands for Solid State Drive, which offers speedy permanent flash memory compared to hard drives.
Optical drives:
Data is read and written using lasers from an optical drive, which serves as secondary storage. Up to 185TB of data can fit inside—for instance, CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray.
USB drives:
USB drives are the most widely used compact, rewritable, removable secondary storage devices.
Magnetic tape:
Magnetic tapes are serial access storage devices with a large data storage capacity typically used for backups.
Characteristics of Secondary Storage
- These memories are magnetic and optical.
- Another name for secondary memory is backup memory.
- Secondary memory is a non-volatile type of memory
- Data is kept indefinitely even after the computer’s power is turned off.
- It helps store data on a computer.
- The machine can run without secondary memory.
- Secondary memory is slower than primary memory.
As we know, data storage is a computer system’s basic functionality. It has two main types, i.e., primary and secondary storage, and primary storage, the central computer system storage. Secondary storage is the computer system’s external storage that stores long-term data.
Here we will study some common differences between primary storage and secondary storage:
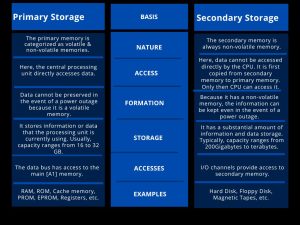
- The memory (Primary and secondary) is where we can store the processed data and instructions that need to be processed.
- Primary is the main memory that accesses data faster than secondary memory. It is an internal memory of a computer system.
- Secondary memory refers to all secondary storage devices that can store large volumes of information.
- There are two primary memory, i.e., RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read Only Memory).
- Types of secondary memory are Hard Drive, SSD, Flash, Optical Drive, USD Drive, and Magnetic Tapes.
- The system cannot run without primary memory. If you face power loss, you can lose data.
- Even after the computer’s power is turned off, data can be permanently preserved in secondary memory.
- Secondary memory is cheaper than primary memory.
Conclusion
In conclusion, primary memory offers actual working space to the processor. It contains the information and commands that the processor is currently processing. Both primary and secondary storage plays a crucial role in the data storage hierarchy and offers quick and effective access to computer resources, but they go about it differently.

