Today, ensuring the safety of online data is critical. Security is always of utmost importance, whether one is accessing sensitive financial information or buying online. Here’s where Secure Sockets Layer, or SSL, comes into play. The Secure Sockets Layer, or SSL, is a mechanism for internet security built on encryption. Developed in 1995 by Netscape with the goal of safeguarding user privacy and data integrity.
But what exactly is SSL, and why is it so important in the realm of network and web security?
The Evolution to TLS
While Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) was pathbreaking in its time, it has since been succeeded by the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. Security is always of utmost importance, whether one is accessing sensitive financial information or buying online. However, the term “SSL” is still commonly used, even when referring to the more modern TLS protocol. Websites now generally use the TLS protocol for secure communications, but the SSL terminology persists.
Understanding the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a security protocol that substantiates encrypted links between a web server and a browser. SSL guarantees the privacy and security of any data transferred between the web server and browser by establishing this encrypted connection. This means that when users enter their personal or payment information, hackers or malicious actors cannot easily access or tamper with that data.
To safeguard sensitive data and ensure the security of online transactions, Netscape first created SSL in the middle of the 1990s. Over time, it became the standard for securing websites and online communications, particularly for businesses and e-commerce platforms.
How SSL Works
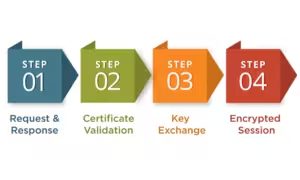
When a user visits a website secured by Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), a series of interactions take place between the web server and the user’s browser. This process, known as the “SSL handshake”, consists of following steps:
- Request and Response: A copy of the server’s SSL certificate is sent back to the browser when it requests a secure connection to a website.
- Certificate Validation: The browser then checks whether the SSL certificate is trustworthy. This verification includes ensuring that the certificate has not expired, is issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA), and matches the website’s domain.
- Key Exchange: Once the SSL certificate is validated, both the browser and the server generate a unique encryption key that will be used for the session.
- Encrypted Session: From this point forward, all data exchanged between the browser and server is encrypted, ensuring that only the intended recipient can decrypt and read the information.
This encryption and authentication process is essential in preventing hackers from intercepting sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, usernames, passwords, and other personal details.
Why is SSL Important for Web Security?
The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol plays a pivotal role in protecting users from cyber threats. Without SSL encryption, data exchanged between a user’s browser and a website is sent in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception by attackers. Here are a few reasons why SSL is crucial for maintaining web security:
- Data Encryption: SSL makes sure that private data, including payment information, login credentials, and personal information, is encrypted. Cybercriminals find it far more difficult to steal or manipulate the data because of its encryption.
- Authentication: SSL certificates provide authentication, which means users can trust they are communicating with the legitimate website they intended to visit. This helps protect users from phishing attacks, where malicious actors create fake websites that mimic legitimate ones.
- Data Integrity: SSL also guarantees data integrity by preventing tampering or corruption of data during transmission. This ensures that the information sent and received remains unaltered.
- Boosting User Trust: Websites that are SSL-secured inform users that their connection is safe by using a padlock icon and “https://” in the URL. This visible indication of security helps build trust, which is essential for businesses and websites that collect sensitive information from users.
Types of SSL Certificates
There are different types of Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates, each serving a specific purpose depending on the level of security a website requires:
- Domain Validated (DV) SSL Certificates: These are the most basic type of SSL certificates, providing encryption but minimal validation. They are suitable for small websites or blogs that don’t handle sensitive information.
- Organization Validated (OV) SSL Certificates: By validating the authority of the company operating the website, OV SSL certificates offer an additional degree of certification. They are ideal for businesses that need to establish trust with their customers.
- Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates: The maximum degree of trust and security is provided by these. With EV SSL, the company’s legal identity is thoroughly verified, and the website’s address bar turns green in some browsers, offering maximum trust for users.
Conclusion
The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) remains one of the most fundamental technologies for ensuring online security. Whether you’re running a small blog or a large e-commerce platform, implementing SSL is crucial to protect both your website and your users. By encrypting data, authenticating users, and maintaining the integrity of the information, SSL helps to create a secure and trustworthy online environment. And while SSL has evolved into TLS, the principles of securing communications and protecting data remain as relevant as ever.
In a world where cyber threats are constantly evolving, having Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or TLS protection is not just an option, it’s a necessity.
Recommended For You: